The obstacle avoiding vehicle project presented here demonstrates a Python script designed to control a robotic vehicle equipped with a sonar sensor. The robot utilizes a servo motor with mounted sonar module to scan its surroundings and adjust its direction based on the detected distances to obstacles. This code exemplifies the integration of hardware control with real-time decision-making in robotics.
By engaging in such projects using Python and our Robo-Tx robotics library, students not only enhance their technical skills but also develop critical thinking, creativity, and teamwork abilities that are valuable in various fields.
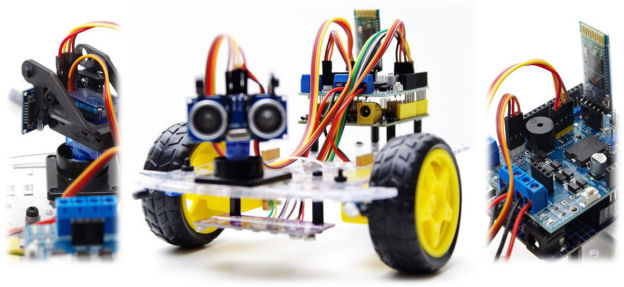
To find out more about the Robo-Tx framework, visit Python Robotics Simplified. Vehicle chassis (such as pictured above) are low cost and easily available as kits from online stores. Such kits usually consist of two motors and wheels, a nylon castor wheel, a chassis board and various fixings. Additionally, an Arduino Uno, a robotics motor expansion board, and a 7.4V LiPo battery will be needed. If not supplied with the vehicle, an HC-05 (or similar) Bluetooth module, 9g servo and SR-04 sonar module (with a panning mount) will also be required.
Download the Project Source Code and Required Utilities
Visit and review Software, Equipment and Tools for Building Robots for instructions to configure your robotics development environment. Use the links in that section to download all robotics project source code (including Robo-Tx firmware) and necessary libraries. Before uploading the Robo-Tx firmware to your Arduino Uno, confirm that SELECTED_PROFILE is set to PROFILE_ROBOT_MOTOR_SHIELD (separated by tab spacing only) in the file Settings.h. Review this profile to discover what else is supported in this configuration.
Connect the servo, sonar and Bluetooth modules to their respective sockets on the motor expansion board. Then, review the steps for changing the Bluetooth module baud rate to 115200 and pairing it to your development computer. Finally, change the Python source file car_obstacle_avoidance.py by setting the value of serial_port to the name of the Bluetooth serial port.
Running the Python source code file results in the robotic vehicle using sonar to avoid and move around obstacles. Refer to the troubleshooting guide if you encounter any problems.
Enhance the Project with Your Own Ideas
The obstacle avoiding vehicle source code has scope for improvement, such as using IR proximity sensors in addition to the sonar module. In the project’s current configuration up to five digital sensors and up to six analog sensors (sharing Arduino pins A0 to A5) are supported. Digital and analog inputs must first be enabled in the Python source code after connection has been established with the Arduino.
# Enable digital input on A2
car.Digital.EnableInputs(2)
# Enable analog input on A0
car.Analog.EnableInputsA(0)
# In other parts of your code
button = car.Digital.IN2.Value
lightSensor = car.Analog.A0.ValueIt is also possible to remotely deploy the Python source code to a Raspberry Pi that acts as the ‘brains’ of the robot. Learn about such remote development possibilities when using Visual Studio code.
Review the other Python robotics projects and refer to the Robo-Tx library help to learn more about reading sensors and controlling actuators. Use the comment section to share ideas or if you have any difficulty.